In order to ensure the reliability and service life of optical fiber communication lines, the temperature characteristics and mechanical characteristics of optical fibers are also two very important physical performance parameters.
1. Temperature characteristics of optical fiber
The loss of an optical fiber can be described by the attenuation coefficient of the optical fiber, and the attenuation coefficient of the optical fiber is directly related to the working environment of the optical fiber communication system, that is, it is increased by the influence of temperature, especially in the low temperature region. The main reason for increasing the attenuation coefficient of optical fiber is the microbending loss and bending loss of the optical fiber.
The microbending loss of the fiber due to temperature changes is caused by thermal expansion and contraction. It is known in physics that the thermal expansion coefficient of silicon dioxide (SiO2) constituting the optical fiber is very small, and it hardly shrinks when the temperature decreases. The optical fiber must be coated and added with other components during the cable forming process. The expansion coefficient of the coating material and other components is large. When the temperature decreases, the shrinkage is more serious. Therefore, when the temperature changes, the expansion coefficient of the material is different. , Will cause the optical fiber to bend slightly, especially in the low temperature region.
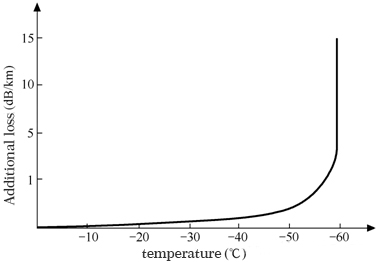
The curve between the additional loss of the fiber and the temperature is shown in the figure. As the temperature decreases, the additional loss of the fiber gradually increases. When the temperature drops to about -55 ° C, the additional loss increases sharply.
Therefore, when designing an optical fiber communication system, it is necessary to consider the high and low temperature cycle tests of the optical cable to check whether the loss of the optical fiber meets the requirements of the index.
2. Mechanical characteristics of optical fiber
In order to ensure that the optical fiber does not break in practical applications and has long-term reliability when used in various environments, it is required that the optical fiber must have a certain mechanical strength.
As is known to all, the material that constitutes the current optical fiber is SiO2, which is to be drawn into 125 μm filaments. During the drawing process, the tensile strength of the optical fiber is about 10 ~ 20kg / mm². The strength can reach 400kg / mm². The mechanical characteristics we want to discuss mainly refer to the strength and life of the fiber.
The strength of the optical fiber here refers to the tensile strength. When the fiber is subjected to more tension than it can withstand, the fiber will break.
As for the breaking strength of optical fiber, it is related to the thickness of the coating layer. When the coating thickness is 5 ~ 10μm, the breaking strength is 330kg / mm², and when the coating thickness is 100μm, it can reach 530kg / mm².
The cause of fiber breakage is due to the defect of the surface of the preform itself during the production process of the optical fiber. When the tension is received, the stress is concentrated on the flaw. When the tension exceeds a certain range, the fiber breaks.
In order to ensure that the optical fiber can have a service life of more than 20 years, the optical fiber should be subjected to a strength screening test. Only optical fibers that meet the requirements can be used for cabling.
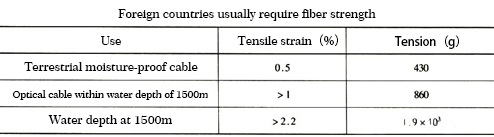
The requirements for fiber strength in foreign countries are shown in the table.
Optical fiber allowable strain includes:
(1) the strain of the optical fiber during cabling;
(2) The strain of the optical fiber caused by some factors when laying the optical cable;
(3) The strain of the optical fiber caused by the change of the working environment temperature.
According to foreign data, when the tensile strain of the optical fiber is 0.5%, its life can reach 20 to 40 years.